
Solar energy refers to the energy derived from the sun’s radiation. It is a renewable and sustainable source of energy that can be harnessed and converted into usable forms of power. The sun emits vast amounts of energy in the form of sunlight, which can be captured and converted into electricity or used for heating purposes.
Solar energy technologies utilize various methods to capture and utilize the sun’s energy. The most common and widely known method is through the use of solar panels or photovoltaic (PV) cells. These panels contain semiconductor materials that convert sunlight directly into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. The generated electricity can be used to power homes, businesses, and even entire cities.
Solar energy can also be utilized for heating applications through the use of solar thermal systems. These systems capture the sun’s heat and use it to heat water, which can be used for domestic purposes or in industrial processes. Solar thermal systems can also be used for space heating, where the collected heat is distributed through a building’s heating system.
Contents
Solar Energy
One of the key advantages of solar energy is its environmental friendliness. It produces no greenhouse gas emissions during operation, unlike fossil fuel-based energy sources. Solar energy is abundant and available in most regions of the world, making it a viable option for sustainable energy generation.
However, the efficiency and availability of solar energy can vary depending on factors such as geographic location, weather conditions, and the type of solar technology used. Advances in solar energy technologies, such as improved efficiency and energy storage capabilities, continue to expand the potential and affordability of solar energy as a clean and renewable energy source.
What is Solar Panel?
A solar panel, also known as a photovoltaic (PV) panel, is a device that converts sunlight into electricity. It is a key component of solar energy systems and plays a crucial role in harnessing solar power for various applications.
Solar panels are typically made up of multiple solar cells, which are made from semiconductor materials such as silicon. These cells contain layers of materials that create an electric field when exposed to sunlight. When photons from sunlight strike the solar cells, they excite the electrons in the semiconductor material, generating a flow of electric current.
The electricity generated by solar panels is in the form of direct current (DC). This DC electricity can be used immediately to power DC devices or stored in batteries for later use. However, most electrical systems in homes and buildings operate on alternating current (AC). To convert the DC electricity from solar panels into AC electricity, an inverter is used. The inverter converts the DC power into AC power, making it compatible with the electrical grid or the appliances and devices in a building.
Solar panels come in various sizes and configurations, ranging from small panels used for charging batteries or powering small devices to larger panels used in residential, commercial, and utility-scale solar power installations. The power output of a solar panel is measured in watts (W) and is influenced by factors such as the size and efficiency of the panel, the amount of sunlight it receives, and the temperature.
Multiple solar panels can be interconnected to form a solar array or a solar panel system. By combining multiple panels, the overall power output can be increased to meet the electricity demands of a specific application, whether it’s a small off-grid system or a large-scale solar power plant.
Solar panels have become increasingly popular as a clean and renewable energy source due to their ability to generate electricity without producing greenhouse gas emissions. They can be installed on rooftops, on the ground, or integrated into various structures, providing a versatile and sustainable energy solution.
How Does Solar Energy Work?
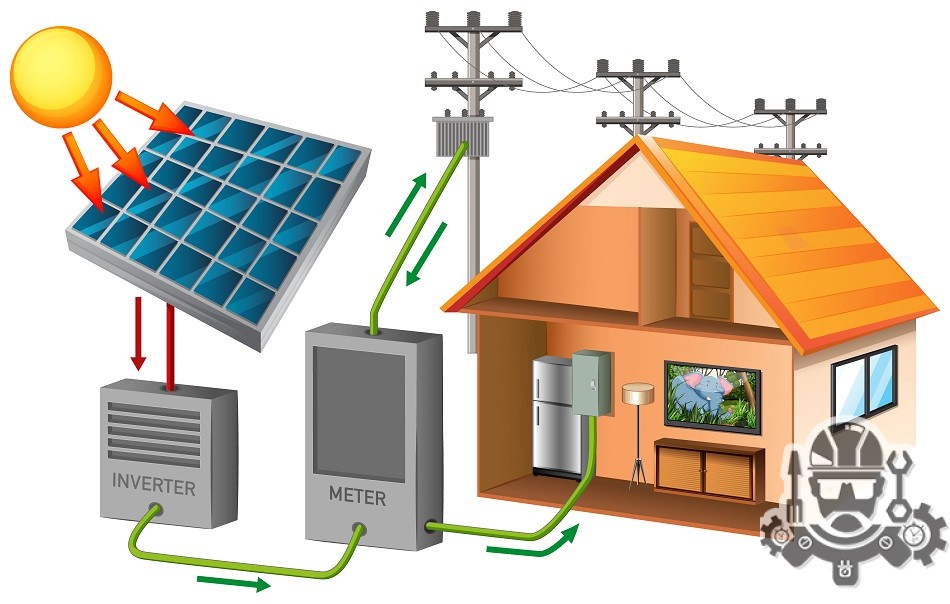
Solar energy works by harnessing the power of sunlight and converting it into usable forms of energy, such as electricity or heat. Here is a general overview of how solar energy systems work:
- Solar Panels: Solar panels, also known as photovoltaic (PV) panels, are composed of multiple solar cells made from semiconductor materials, typically silicon. When sunlight hits the solar panels, the photons in the sunlight excite the electrons in the solar cells, generating a flow of direct current (DC) electricity.
- Inverter: The DC electricity generated by solar panels is then sent to an inverter. The inverter converts the DC electricity into alternating current (AC) electricity, which is the standard form of electricity used in homes, businesses, and the electrical grid.
- Electrical Load or Grid Connection: The AC electricity from the inverter is either used to power electrical loads within the building or fed into the electrical grid. When the solar energy system generates more electricity than is needed, the excess power can be sent back to the grid for others to use, often earning credits or compensation through net metering or feed-in tariff programs.
- Net Metering (if applicable): In regions with net metering policies, any excess electricity produced by the solar energy system can be exported to the grid and credited to the system owner’s electricity bill. During times when the solar system is not producing enough electricity, such as at night, the system owner can draw electricity from the grid.
- Monitoring and Control: Solar energy systems often include monitoring and control components that track the system’s performance, energy production, and any potential issues. This allows system owners to monitor the efficiency and output of their solar panels.
In addition to producing electricity, solar energy can also be used for solar thermal applications. Solar thermal systems capture the sun’s heat and use it for water heating, space heating, or industrial processes. These systems typically use solar collectors, which absorb sunlight and transfer the heat to a fluid, which can then be used for various heating purposes.
It’s important to note that the efficiency and effectiveness of solar energy systems can be influenced by factors such as the availability of sunlight, the angle and orientation of the solar panels, the efficiency of the panels, and any shading or obstructions that may affect sunlight exposure.
Overall, solar energy provides a sustainable and renewable source of power, reducing dependence on fossil fuels and contributing to a cleaner and more sustainable energy future.
Cost of Installing Solar Energy on the Roof of the House

The cost of installing solar energy on the roof of a house can vary depending on several factors, including the size of the system, location, local incentives, and the complexity of the installation. Here are some key cost considerations:
- System Size: The size of the solar energy system is typically measured in kilowatts (kW) or kilowatt-hours (kWh). Larger systems will generally cost more than smaller systems. The system size needed will depend on factors such as the electricity consumption of the household and the available roof space for solar panels.
- Equipment and Components: The cost of solar panels, inverters, mounting systems, wiring, and other components required for the installation will contribute to the overall cost. The quality and efficiency of the equipment can also affect the price.
- Installation Labor: The cost of labor for the installation will depend on factors such as the complexity of the installation, the size of the system, and the location of the house. Labor costs can vary between different regions and installation companies.
- Permitting and Interconnection: There may be costs associated with obtaining permits, inspections, and interconnection agreements with the local utility company. These costs can vary depending on the location and local regulations.
- Additional System Features: Optional features such as battery storage systems or monitoring systems may add to the overall cost of the installation.
- Incentives and Rebates: Depending on the location, there may be federal, state, or local incentives, tax credits, or rebates available for installing solar energy systems. These incentives can help offset the upfront costs and reduce the overall expenses.
It is important to note that the cost of solar energy systems has been decreasing over the years due to advancements in technology and increased market competition. Additionally, the return on investment (ROI) of a solar energy system should be considered, as it can provide long-term savings on electricity bills.
To get an accurate estimate of the cost for installing solar energy on a specific house, it is recommended to contact local solar installation companies or use online solar calculators that take into account various factors such as location, system size, and available incentives. They can provide customized quotes and financial analysis based on the specific circumstances of the project.
Solar energy refers to the energy derived from the sun's radiation. It is a renewable and sustainable source of energy that can be harnessed and converted into usable forms of power. The sun emits vast amounts of energy in the form of sunlight, which can be captured and converted into electricity or used for heating purposes.
A solar panel, also known as a photovoltaic (PV) panel, is a device that converts sunlight into electricity. It is a key component of solar energy systems and plays a crucial role in harnessing solar power for various applications.
Solar energy works by harnessing the power of sunlight and converting it into usable forms of energy, such as electricity or heat. Here is a general overview of how solar energy systems work:



